AIS GIS RMU Production lines
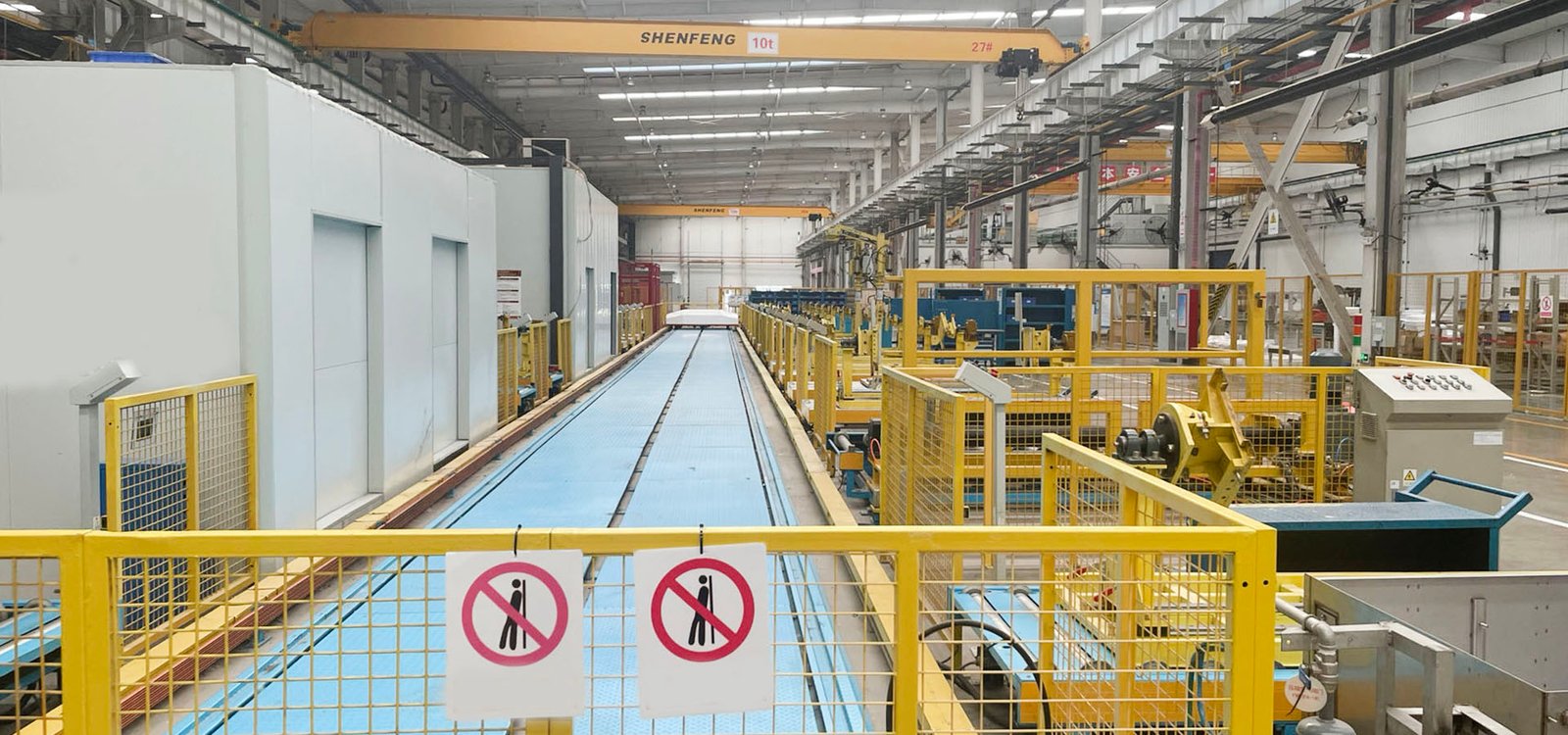

AIS (Air Insulated Switchgear), GIS (Gas Insulated Switchgear), and RMU (Recloser or Sectionalizer) are high-voltage electrical equipment with distinct production line requirements due to their unique structural and operational characteristics. Here’s an overview of the production line equipment typically used for each:
AIS Production Line Equipment:
- Assembly Jigs and Fixtures: Specific to the design of AIS components, these are used to hold parts in place during assembly.
- Insulation Handlers: Devices to safely handle porcelain insulators and other insulating materials to prevent damage and ensure correct placement.
- Circuit Breaker Assemblers: Specialized machinery to assemble the circuit breakers with precision, including the placement of contacts and mechanisms.
- Welding Equipment: For joining metal components of the AIS, ensuring structural integrity and durability.
- Coating and Painting Systems: To apply protective coatings to the AIS components to safeguard against environmental factors.
- Testing Stations: For conducting dielectric tests, contact resistance tests, and other functional tests to ensure the AIS meets performance standards.
GIS Production Line Equipment:
- Gas Handling Systems: To manage the SF6 gas used for insulation within the GIS, including filling, evacuation, and leak testing.
- Module Assemblers: For assembling the gas-tight modules that make up the GIS, ensuring precision and gas-tight seals.
- CNC Machines: Computer Numerical Control machines for high-precision cutting and shaping of metal components.
- Clean Rooms: Since GIS components require a high level of cleanliness to prevent contamination, clean room environments are essential during assembly.
- Sealing and Gasketing Equipment: For applying seals and gaskets to ensure the gas-tight integrity of the GIS compartments.
- Integrity Test Systems: To perform pressure tests and verify the leak-tightness of the assembled GIS modules.
RMU Production Line Equipment:
- Automated Assembly Lines: For the efficient assembly of RMU components, including automated guidance systems for positioning parts.
- Electronics Assemblers: Specialized for assembling the electronic control systems of RMU, including microprocessor-based controllers.
- Cable Management Systems: To organize and secure the wiring within the RMU for neatness and reliability.
- Load Test Equipment: For simulating the operational loads on the RMU to ensure mechanical and electrical stability under stress.
- Environmental Test Chambers: To test RMU performance under various environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and vibration.
- Calibration Tools: For calibrating the timing mechanisms and other adjustable parameters in the RMU to ensure accurate operation.
Each of these production lines requires a combination of skilled labor, automated machinery, and stringent quality control processes to ensure that the final product meets the high standards required for high-voltage electrical applications. Additionally, safety measures are paramount throughout the production process due to the high voltages and potential hazards involved in the manufacturing of such equipment.
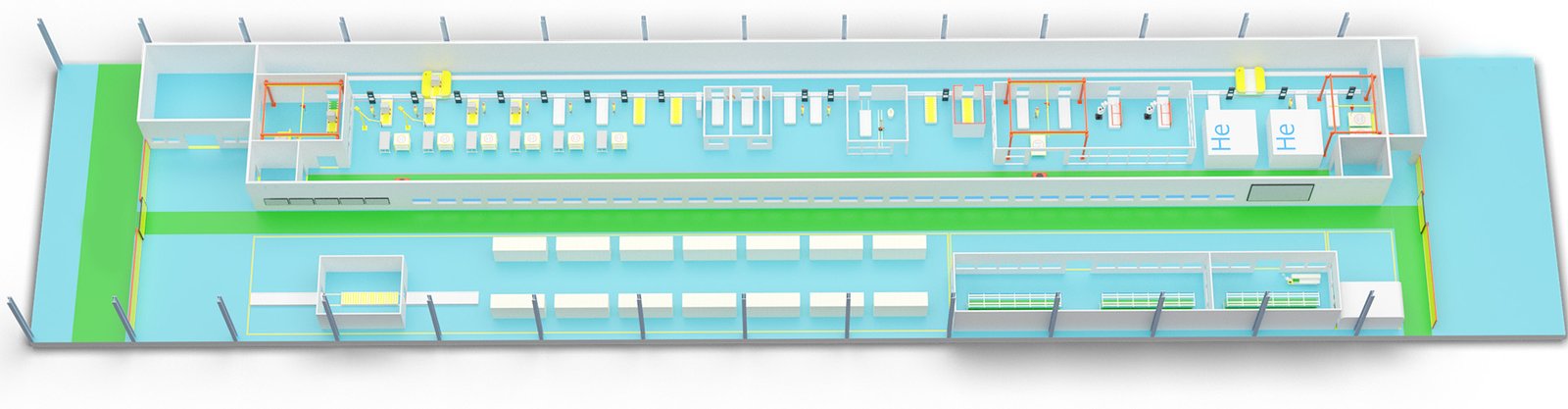
Regarding the production line of AIS (Air Insulated Switchgear), GIS (Gas Insulated Switchgear), and RMU (Recloser or Sectionalizer) types of high-voltage electrical equipment, we can discuss it from the following aspects:
- Product Structural Features:
- GIS equipment is widely used in power grids above 110kV due to its compact structure, space-saving, and easy maintenance. GIS equipment is divided into several gas compartments according to the different functions of each component, to meet the different pressure requirements of SF6 gas for different components.
- AIS equipment, with porcelain casing as the equipment shell and external insulation, optimizes investment costs but occupies a larger area and is more susceptible to the impact of climatic conditions.
- Assembly and Testing Process:
- The production line of high-voltage electrical equipment typically includes component preparation, assembly, wiring, insulation treatment, testing, adjustment and calibration, and packaging steps.
- The assembly process requires high precision and strict quality control to ensure the performance and reliability of the equipment.
- The testing phase includes functional testing and reliability testing to ensure that the equipment can work according to the expected requirements and maintain stability and durability under long-term operation or different environmental conditions.
- Technological Advancements:
- Since the introduction of GIS technology in the 1960s, it has been continuously developing, maintaining high reliability while reducing material usage and cost. For example, the development of circuit breaker technology has increased capacity while reducing the number of break points, simplifying the structure, improving reliability, and reducing the use and emission of SF6 gas.
- The use of intelligent monitoring and diagnostic tools extends the maintenance cycle and avoids unnecessary work, improving operational reliability and saving maintenance costs.
- Industry Chain:
- In the ultra-high voltage industry chain, GIS, as a part of the transmission lines and equipment in the middle reaches, accounts for a significant proportion of the value in the core equipment of ultra-high voltage alternating current systems.
- Industry Status:
- The production of high-voltage switchgear has been generally stable, but the growth rate is not high. The production volume of high-voltage switchgear in recent years has shown the maturity of the market and the demand for efficient and reliable equipment.
From the above information, we can see that the production line of AIS, GIS, and RMU high-voltage electrical equipment not only focuses on the structural features and technological innovation of the products but also emphasizes the precision and reliability of the assembly and testing process to meet the demand for high-performance switchgear in modern power grid construction.
