Vacuum circuit breaker structure and production line
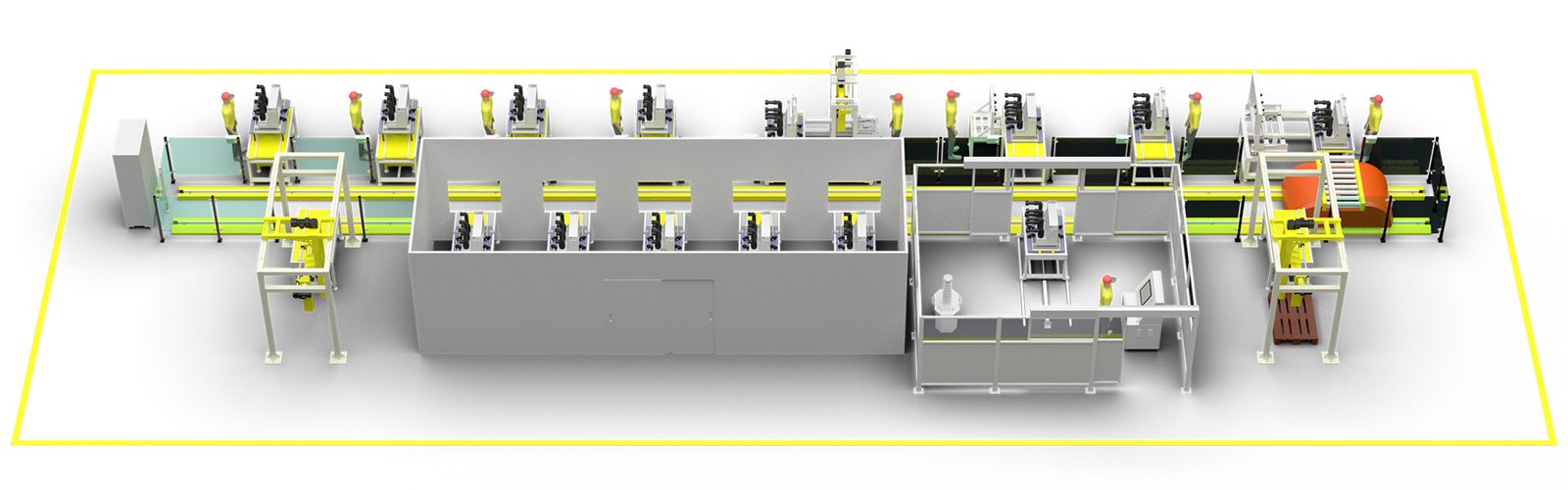
The vacuum circuit breaker production line is an automated facility specifically designed for manufacturing high-voltage vacuum circuit breakers. It integrates robotic arms, automatic lifting and flipping devices, and other mechanisms to reduce the intensity of manual labor. The line operates automatically through a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) system, encompassing stages such as characteristic testing, mechanical run-in, and secondary circuit assembly. Advanced sensors and testing equipment are employed to ensure product quality and increase production efficiency. Additionally, the production line features remote monitoring capabilities, enabling paperless management of production records.
Vacuum circuit breakers are a type of high-voltage switching equipment, known for their compact size, light weight, high breaking capacity, and long life, primarily due to the use of high vacuum as the arc-quenching medium. The structure of a vacuum circuit breaker generally includes sealed-off poles, operating mechanisms, casing, spring assembly, and secondary circuit assembly.
Structural Components:
- Sealed-off Poles: The poles encapsulate the vacuum interrupter and the primary electrical circuit in epoxy resin, enhancing insulation reliability.
- Operating Mechanism: Responsible for the closing and tripping operations of the circuit breaker, often including closing and tripping modules.
- Casing: Protects internal components and ensures stable operation of the equipment.
- Spring Assembly: Provides the power necessary for the operation of the circuit breaker.
- Secondary Circuit Assembly: Responsible for the control and signal transmission of the circuit breaker.
Assembly Process:
- Main Shaft Assembly: Assembling the main shaft part of the circuit breaker.
- Mechanism Assembly: Integrating the operating mechanism with the main shaft.
- Phase Column Pre-assembly: Preparing and pre-assembling the phase columns.
- Chassis Assembly: Assembling the chassis part of the circuit breaker.
- Characteristic Testing: Conducting performance tests on the circuit breaker.
- Mechanical Run-in: Ensuring smooth operation of the mechanical parts of the circuit breaker.
- Secondary Circuit Assembly: Completing the assembly of the control circuit of the circuit breaker.
- Final Inspection: Conducting a final check on the assembled circuit breaker.
Automated Production Line:
Automated production lines are key to the efficient production of vacuum circuit breakers. According to the search results, the basic working environmental conditions for the VS1 production line are dryness, and the temperature range is -10°C to 50°C. The technical parameters of the production line include the total length, total width, effective working height, and workstation length, which are customized according to customer needs and assembly processes. The structural configuration of the production line involves the main line, tooling board, guide edges, power sockets, gas lines, body color, gas source, plug boards, water pipe routes, and DC power supply.
Features of the automated production line include:
- High Integration: Integrating the circuit breaker status monitoring module and motor control module into one control box simplifies installation and maintenance.
- Intelligent Unit: Employing advanced signal monitoring technology and microprocessor technology for status monitoring and comprehensive alarm functions.
- Electric Chassis Car: Providing electric operation capabilities to achieve intelligent, programmable, and remote-controlled switchgear.
- Wireless Temperature Measurement Device: Using a hoop-type sensor and wireless transmission technology for measuring and monitoring the temperature of the circuit breaker’s contacts.
Automated production lines are crucial for mass production of vacuum circuit breakers by reducing manual operations, improving production efficiency, and ensuring product quality. By integrating advanced sensors, control systems, and robotic arms, automated production lines can achieve efficient production rhythms while ensuring product consistency and reliability.
