Layout of Vacuum Circuit Breaker Production Line
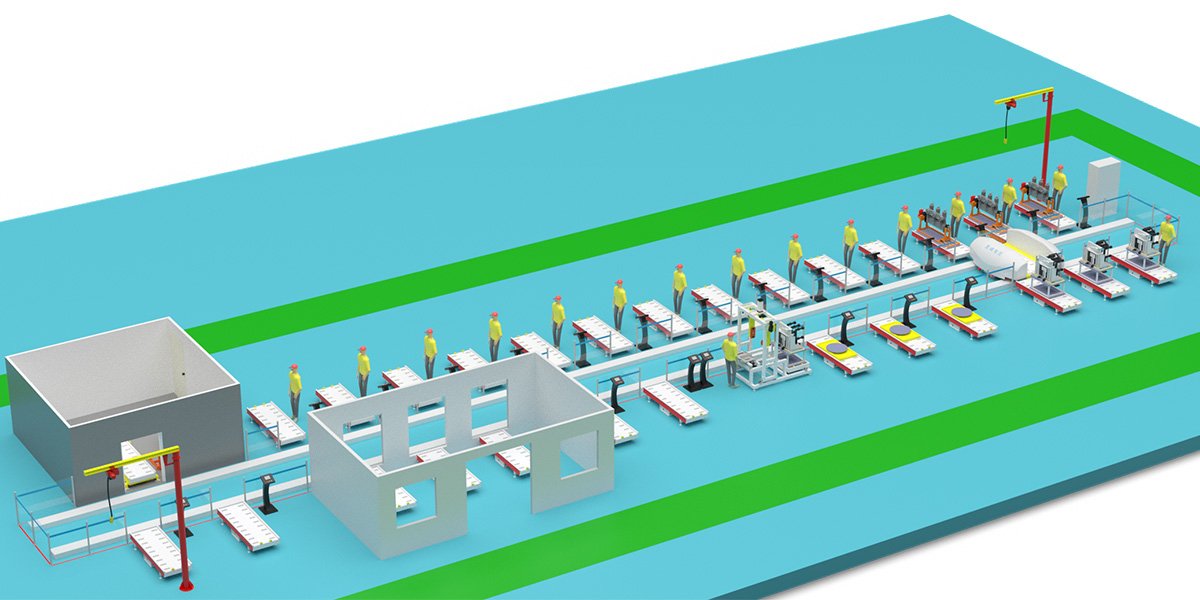
Vacuum circuit breakers are a type of high-voltage electrical apparatus that utilize vacuum as both an insulating and arc-extinguishing medium. They are known for their simple structure, compact size, light weight, minimal maintenance, and long service life. Below is a detailed introduction to the structure of vacuum circuit breakers and their assembly and production technology:
Structure of Vacuum Circuit Breakers
A vacuum circuit breaker mainly consists of the following parts:
- Vacuum Arc Chamber: The vacuum arc chamber is the core component of the vacuum circuit breaker, containing a pair of contacts. When current passes through, an electric arc is generated between the contacts. The vacuum environment quickly extinguishes the arc, achieving the interruption of the electrical circuit.
- Operating Mechanism: The operating mechanism is used to control the opening and closing of the vacuum circuit breaker, including closing and opening electromagnets, transmission mechanisms, energy storage mechanisms, etc.
- Bracket and Insulators: The bracket is used to fix the vacuum arc chamber and operating mechanism, while insulators provide the necessary electrical insulation.
- Auxiliary Switches and Earthing Switches: Auxiliary switches are used to send signals indicating the open and closed positions, and earthing switches ensure equipment safety.
- Secondary Control Circuit: This includes control cables, terminals, relays, auxiliary switches, etc., used to achieve remote control and protective functions.
Assembly and Production Technology of Vacuum Circuit Breakers
The production process of vacuum circuit breakers typically includes the following main steps:
- Main Shaft Assembly: First, the main shaft assembly and buffer are installed in the casing according to the production plan and customer order. After ensuring the assembly is correct, the casing is moved to the next process in the production line.
- Mechanism Assembly: The assembly of the vacuum circuit breaker’s mechanism takes place, including the pre-assembly of the closing and opening mechanisms, the installation of support rods and copper sleeves, and the rotation of the half-axis.
- Casing and Spring Assembly: The assembly of the closing and opening springs is completed, ensuring the correct installation and accuracy of the spring forces.
- Pre-assembly and Assembly of Phase Columns: Pre-assembly of the internal flexible connections, double-headed rods, and insulators of the phase columns takes place, followed by the assembly of the phase columns onto the casing and connection to the operating mechanism.
- Secondary Circuit Assembly: The assembly of the auxiliary control circuit of the circuit breaker is completed, ensuring that each circuit is correctly wired without error.
- Mechanical Run-in: The mechanical run-in is performed on the vacuum circuit breaker to remove any burrs from the mechanism and ensure smooth operation.
- Final Inspection and Testing: Various performance tests are conducted on the assembled vacuum circuit breaker, including insulation resistance tests, operating tests, and voltage withstand tests, to ensure the product meets technical standards and customer requirements.
