GIS Assembly Line Layout
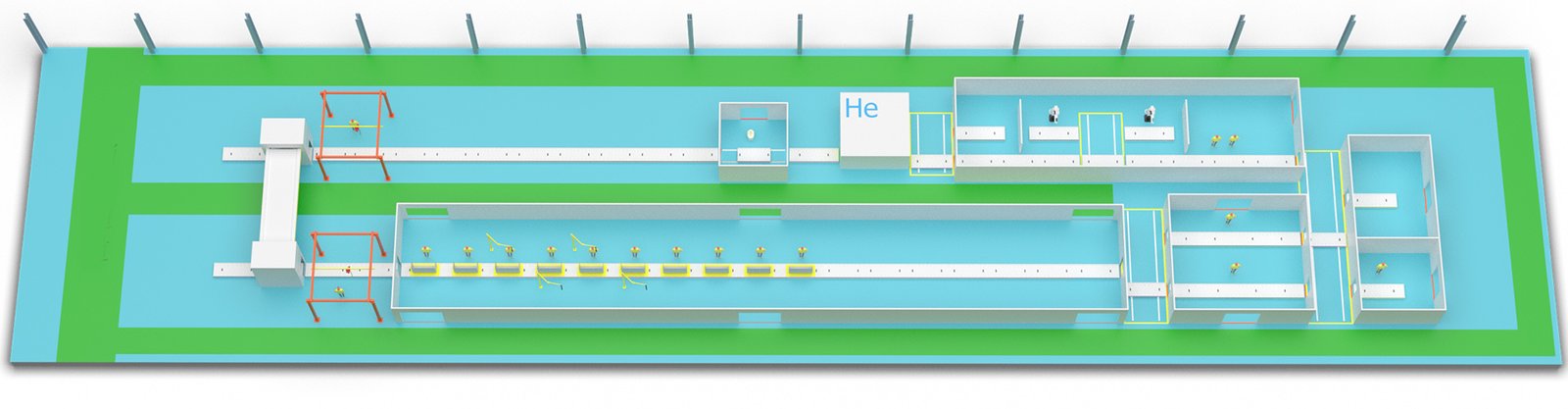
The assembly line process for GIS can be summarized as follows: 1. Fabricate the gas chamber using 3.0mm thick stainless steel plates to ensure hermetic sealing; 2. Pre-install high-voltage components such as circuit breakers; 3. Assemble into a cabinet structure with stainless steel fasteners; 4. Conduct automatic gas filling and leak detection to ensure hermeticity; 5. Perform withstand voltage and lightning impulse tests to verify insulation performance; 6. Finally, conduct a functional and performance inspection before leaving the factory to ensure product compliance.
The structural, assembly, and testing process for an inflatable cabinet (also known as gas-insulated switchgear) can be summarized as follows:
Gas Chamber Fabrication: The gas chamber, made from 3.0mm thick stainless steel, is fabricated using high-precision robotic welding to ensure hermetic sealing.
Component Installation of gas-insulated switchgear: High-voltage components such as circuit breakers, current transformers, and other necessary equipment are pre-installed within the gas chamber.
Cabinet Assembly: The gas chamber is assembled into a cabinet structure, which includes the division of the cable chamber using stainless steel side panels and partitions, followed by the assembly of the cable chamber floor.
Fastening: All fasteners are made of stainless steel to ensure secure and stable connections.
Hermeticity Testing for gas-insulated switchgear: The gas chamber undergoes a hermeticity test using fully automatic inflation and leak detection equipment to ensure there are no leaks.
Withstand Voltage Testing: The cabinet is subjected to power frequency withstand tests to verify the insulation level and ensure it meets safety standards.
Lightning Impulse Testing: This test checks the insulation’s ability to withstand high-voltage surges, simulating lightning strikes.
Partial Discharge Testing: This test is conducted to detect any partial discharges within the insulation material, which could indicate potential failure points.
Final Inspection: Before leaving the factory, the cabinet undergoes a final inspection that includes checking the installation of all components and fasteners, verifying the functionality of the cabinet, and ensuring all operations are performed correctly and repeatedly.
The use of an assembly line for the production and testing of GIS offers numerous benefits, including streamlined workflow, enhanced efficiency, and reduced production time. It ensures consistent quality through standardized operations and facilitates easy identification of defects. Additionally, an assembly line allows for better utilization of resources, cost savings, and improved safety standards by separating hazardous operations. It also enables the implementation of advanced automation, contributing to higher precision and reliability in the final product.
