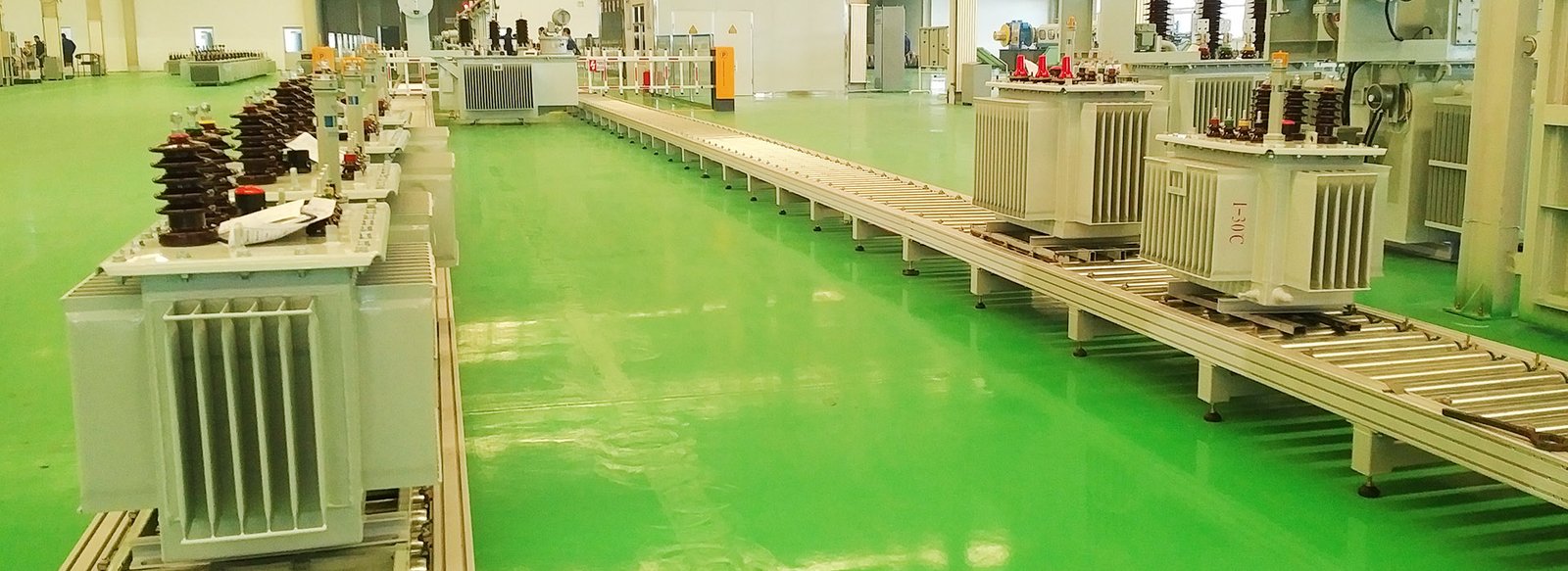

The process flow of power transformer production line is a series of fine and complex steps aimed at ensuring the high quality and performance of transformers. The main process flow of the power transformer production line is as follows:
1. Material preparation
Before production begins, all necessary materials need to be prepared, including silicon steel sheets, copper or aluminum wires, insulation materials, oil tanks, and storage tanks. The selection of these materials is crucial for the performance and durability of transformers.
2. Coil winding
The coil is the core part of a transformer, and its manufacturing process includes installing the winding skeleton, winding the coil, wire welding, insulation wrapping, coil shaping, and coil testing. The quality of the coil directly affects the efficiency and reliability of the transformer.
3. Iron core assembly
The manufacturing of iron cores includes cutting silicon steel sheets, deburring, stacking iron cores, installing pull plates and shielding, tying iron cores, and conducting core testing. The quality of the iron core has a significant impact on the magnetic flux and loss of transformers.
4. Insulation processing
The processing of insulation components includes cutting, deburring, chamfering, and moisture-proof treatment. Insulation components are crucial for ensuring the safe operation of transformers and preventing electrical faults.
5. Processing of oil tanks and storage tanks
The processing of oil tanks and storage tanks involves steel plate cutting, welding, rust removal, sandblasting, primer painting, painting, and mechanical strength testing. These steps ensure the durability and protective performance of the fuel tank.
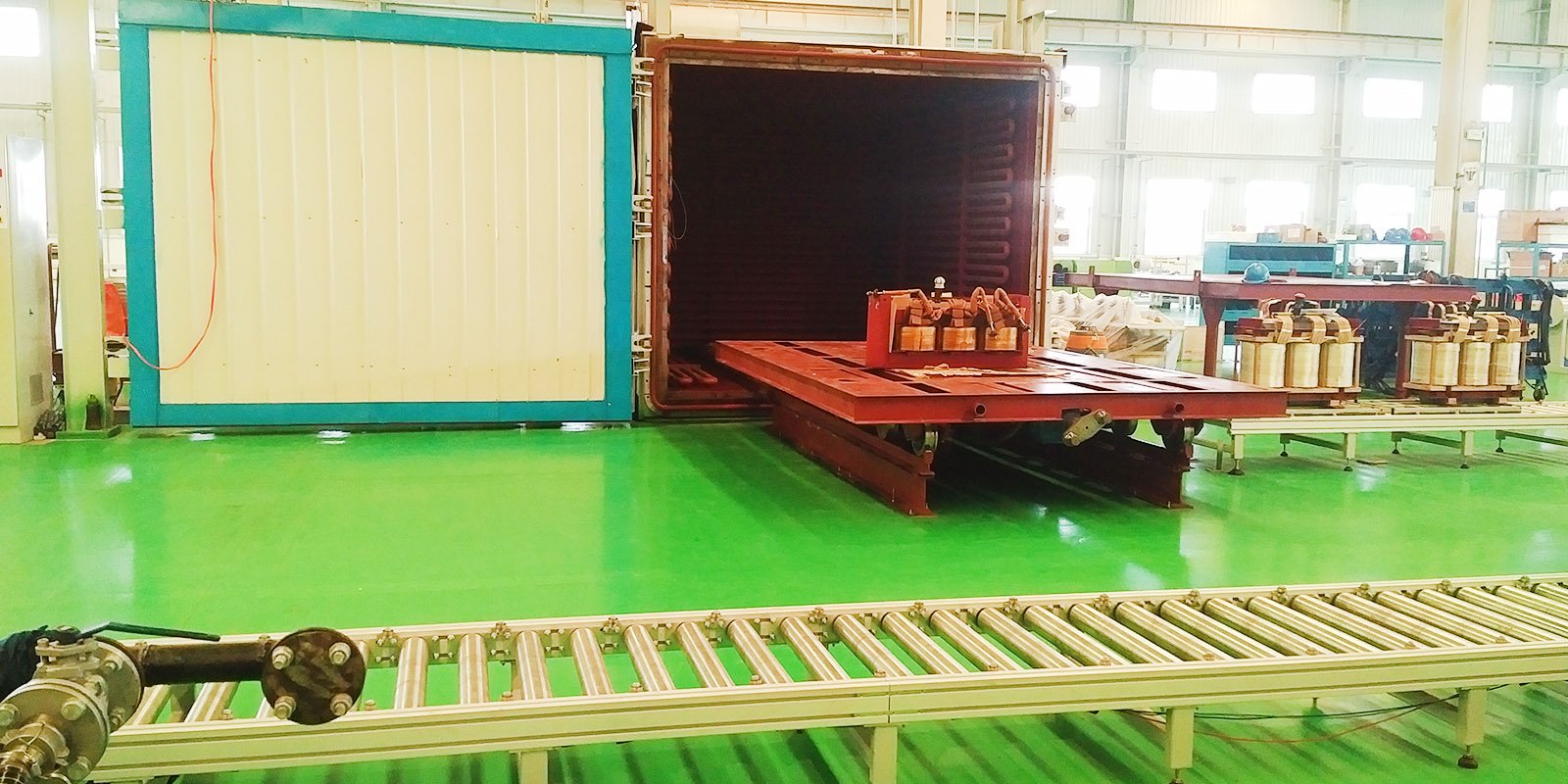

6. General Assembly
General assembly is the process of integrating all components together, including installing iron cores, oil tank pipelines, coils, stacking iron yokes, installing tap changers, welding leads, wrapping lead insulation, semi-finished product testing, body drying, organizing body, oil tank assembly, accessory assembly, oil injection, sealing test, and hot oil circulation.
7. Testing and debugging
After the transformer assembly is completed, a series of tests are required, including electrical performance testing, insulation strength testing, and error calibration, to ensure that the transformer meets the specified technical parameters and performance standards.
8. Packaging and factory inspection
Finally, the transformer needs to be appropriately packaged for transportation and storage. Before leaving the factory, a final quality inspection is required to ensure that the product is defect free and meets all requirements.
Through these carefully designed and strictly controlled process flows, the power transformer production line can produce transformers with excellent performance, safety, and reliability, meeting the needs of the power system.
